All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The pso Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the pso Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The pso and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The PsOPsA Hub is an independent medical education platform, supported by educational grants. We would like to express our gratitude to the following companies for their support: UCB, founding supporter. The funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis content recommended for you
The safety and efficacy of spesolimab in Asian patients
Spesolimab is a humanized, selective antibody, which disrupts the activation of the interleukin-36 receptor.1 The interleukin-36 pathway is involved in the pathogenesis of multiple inflammatory diseases, including generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) in adults.
Spesolimab has been approved for use in multiple countries, including Japan, mainland China, and the European Union,1 as well as receiving approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of GPP flares in September 2022, as summarized by the Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Hub here.1
The Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Hub has previously reported on the safety and frequency of adverse events following treatment with spesolimab in the GPP population from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial, Effisayil™ 1 (NCT03782792). Here, we summarize the safety and efficacy findings from the Effisayil™ 1 clinical trial in respect to the characteristics and outcomes of the 29 Asian participants, as reported by Morita et al.2 in The Journal of Dermatology.
Patient characteristics
The baseline characteristics among Asian patients in the spesolimab treatment and placebo groups were comparable. However, there was a greater number of female participants in the placebo group (Table 1).
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of Asian participants*
|
GPPGA, Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment. |
||
|
Characteristic, % (unless otherwise stated) |
Spesolimab |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Mean age, years |
42.2 |
43.2 |
|
Mean body weight, kg |
68.1 |
64.0 |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
Female |
62.5 |
92.3 |
|
Male |
37.5 |
7.7 |
|
Country of enrollment |
|
|
|
China |
12.5 |
30.8 |
|
Japan |
6.3 |
7.7 |
|
Malaysia |
50.0 |
30.8 |
|
Singapore |
0.0 |
7.7 |
|
Thailand |
0.0 |
7.7 |
|
Taiwan |
18.8 |
15.4 |
|
France |
12.5 |
0.0 |
|
Present or past psoriasis†,‡ |
75.0 |
76.9 |
|
Ongoing plaque psoriasis |
25.0 |
15.4 |
|
GPPGA total score |
|
|
|
3 |
68.8 |
100.0 |
|
4 |
31.3 |
0.0 |
|
GPPGA pustulation subscore |
|
|
|
2 |
18.8 |
30.8 |
|
3 |
43.8 |
46.2 |
|
4 |
37.5 |
23.1 |
Efficacy
The primary endpoint in this study was a Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA) pustulation subscore of 0, defined as no visible pustules at Week 1. This primary endpoint was met in 62.5% of patients in the spesolimab group compared with 7.7% in the placebo group (risk difference, 54.8; 95% confidence interval, 17.3–79.8). A secondary endpoint of a GPPGA total score of 0 or 1 (demonstrated by clear or almost clear skin) at Week 1 was met in 50.0% and 15.4% of patients in the spesolimab and placebo group, respectively (risk difference, 34.6; 95% confidence interval, −3.1 to 64.7). The comparisons of GPPGA pustulation subscore and GPPGA total score between the spesolimab and placebo groups among Asian patients and the overall population are outlined in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Percentage of Asian patients and patients in the overall population with a GPPGA pustulation subscore of 0 or a GPPGA total score of 0 or 1 at Week 1*
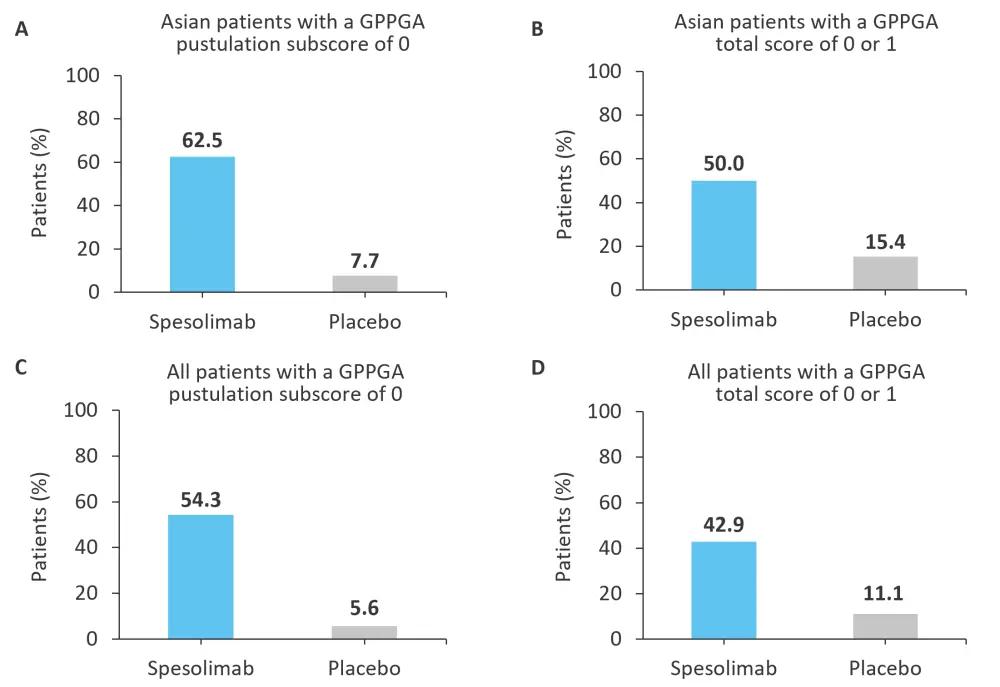
GPPGA, Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment.
*Adapted from Morita, et al.2
Safety
Among Asian patients, adverse events (AEs) were reported in 68.8% of patients in the spesolimab group compared with 61.5% of patients in the placebo group at Week 1. Common AEs in the spesolimab group included urinary tract infections and peripheral edema, occurring in 12.5% of patients. In the placebo group, the more common AEs included pyrexia and dizziness, occurring in 23.1% and 15.4% of patients, respectively. No deaths were recorded in this study. Other reported AEs are displayed in Table 2.
Table 2. Adverse events occurring in Asian patients*
|
AE, adverse event; RCTC, Rheumatology Common Toxicity Criteria. |
||
|
Event, % |
Spesolimab |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Any AE |
68.8 |
61.5 |
|
Common AE† |
|
|
|
Urinary tract infection |
12.5 |
0.0 |
|
Headache |
6.3 |
7.7 |
|
Extremity pain |
6.3 |
7.7 |
|
Diarrhea |
6.3 |
0.0 |
|
Pyrexia |
6.3 |
23.1 |
|
Peripheral edema |
12.5 |
7.7 |
|
Dizziness |
0.0 |
15.4 |
|
Nausea |
6.3 |
0.0 |
|
Severe AE (RCTC Grade 3 or 4) |
0.0 |
7.7 |
|
Investigator-defined drug-related AE |
31.3 |
38.5 |
|
Serious AE‡ |
6.3 |
0.0 |
|
Serious AE requiring or prolonging hospitalization |
6.3 |
0.0 |
Conclusion
Overall, the majority of characteristics and treatment outcomes among Asian patients were comparable with the overall population. Spesolimab treatment was found to improve outcomes in Asian patients compared with a placebo for GPP flares, as well as having an acceptable safety profile. The data retrieved from this analysis of the Asian participants in the Effisayil™ 1 clinical trial support the approved use of spesolimab to treat GPP in Asian patients.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with plaque psoriasis do you see per month?



