All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The pso Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the pso Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The pso and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The PsOPsA Hub is an independent medical education platform, supported by educational grants. We would like to express our gratitude to the following companies for their support: UCB, founding supporter. The funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis content recommended for you
Improvement in PROs after 3-year treatment with ustekinumab or TNFi: Results from the real-world PsABio study
Do you know... In the real-world PsABio study, patients who achieved cDAPSA low disease activity/remission, minimal disease activity, and very low disease activity following 3 years of consistent ustekinumab or TNFi treatment, versus those that did not achieve these endpoints, experienced:
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) affects ~30% of patients with psoriasis.1 PsA can cause pain, fatigue, and swollen and tender joints, which can impact quality of life.1 To provide a comprehensive understanding of treatment effectiveness, it is important to use patient reported outcomes (PROs) as a measurement of physical, psychological, and social functioning, alongside physician assessments in long-term clinical trials of PsA. Here, we summarize key findings from the multinational, prospective, real-world PsABio study (NCT02627768) which evaluated PROs after 3 years of treatment with ustekinumab or a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi).
Study design
The final analysis of PsABio included 895 adult patients, with 439 randomized to ustekinumab and 456 randomized to TNFi. Of these, 219 receiving ustekinumab and 218 receiving TNFi remained on their original treatments for 3 years; the remainder switched or stopped treatment before this time. The following PROs were evaluated in patients who remained on treatment for 3 years:
- EuroQol-5 dimensions questionnaire (EQ‑5D)‑3L health state: EQ-5D and EQ visual analog scale (EQ VAS)
- 12-item PsA Impact of Disease questionnaire (PsAID-12)
- Work Productivity and Activity Impairment for PsA questionnaire (WPAI)
- Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA)
Results
Baseline patient characteristics for patients who remained on the same treatment for 3 years are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Key baseline patient characteristics*
|
bDMARD, biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug; BMI, body mass index; cDAPSA, Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. *Adapted from Gossec, et al.1 |
||
|
Characteristic, % (unless otherwise stated) |
Ustekinumab |
TNFi |
|---|---|---|
|
Mean age, years |
51.5 |
46.7 |
|
Mean BMI, mg/m2 |
28.9 |
27.1 |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
Male |
48.4 |
56.0 |
|
Female |
51.6 |
44.0 |
|
Mean time since initial diagnosis, years |
7.7 |
6.4 |
|
Line of bDMARD |
|
|
|
First-line |
49.8 |
59.2 |
|
Second-line |
32.4 |
31.7 |
|
Third-line |
17.8 |
9.2 |
|
Mean cDAPSA score, n |
30.3 |
30.3 |
Patient-reported outcomes
Mean change from baseline to year 3 in EQ-5D score and overall PsAID-12 score are shown in Figure 1. EQ-5D and PSAID-12 scores improved across the 3 years for both treatments.
Figure 1. Mean score change from baseline to Year 3 in A PsAID-12 and B EQ-5D*
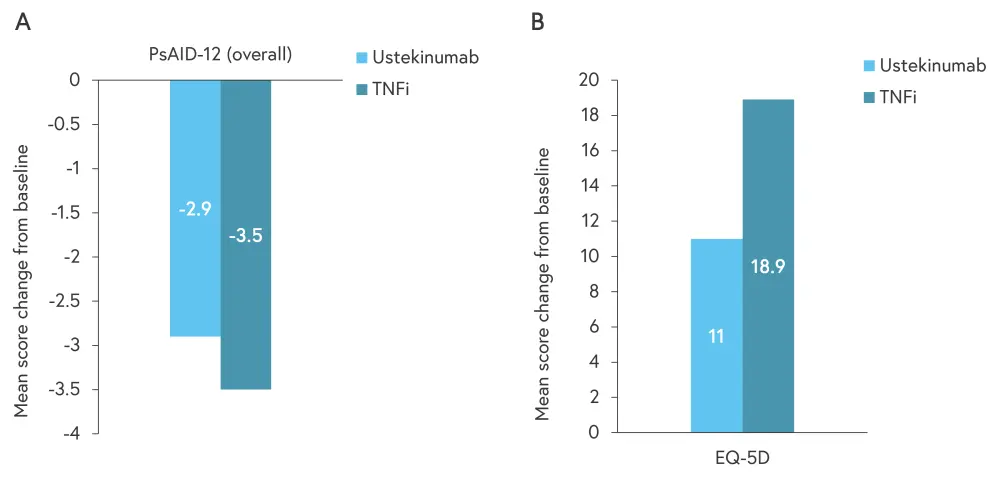
EQ-5D, EuroQol-5 dimensions questionnaire; PsAID-12, 12-item PsA Impact of Disease questionnaire; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
*Adapted from Gossec, et al.1
The percentage of patients employed at baseline and year 3 was similar in both treatment groups (54.5% and 55.9% for the ustekinumab group and 61.5% and 64.1% in the TNFi group, respectively). Patients treated with a TNFi had greater changes in WPAI outcomes compared with patients treated with ustekinumab; however, they also started from a lower baseline for each outcome. Mean changes in WPAI outcomes from baseline to year 3 are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Mean score change from baseline to Year 3 in WPAI outcomes*
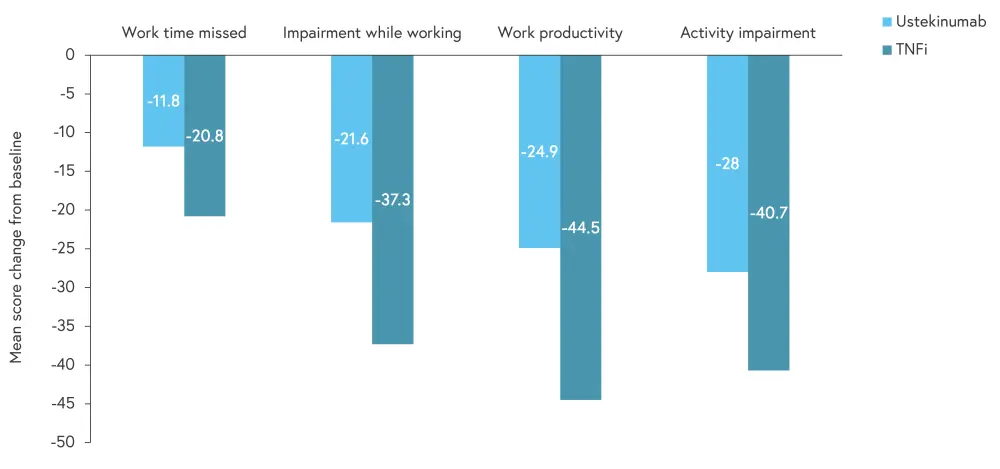
TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
*Adapted from Gossec, et al.1
Link between PROs and efficacy endpoints
At 6 months and 3 years, patients who achieved cDAPSA low disease activity/remission had higher (better) EQ-5D scores compared with patients who did not achieve this endpoint. Similarly, patients who achieved cDAPSA low disease activity/remission had lower (better) PsAID-12 scores at Month 6 and Year 3 compared with those that did not achieve this endpoint. Work impairment scores, as measured by WPAI outcomes, were lower (better) at 6 months in patients achieving cDAPSA low disease activity/remission, minimal disease activity, and very low disease activity vs those not achieving these endpoints; similar scores were observed at 3 years.
Conclusion
Over 3 years of the PsABio real-world study, patients treated with both ustekinumab and TNFis demonstrated an improvement in PROs. Over the 3 years, work productivity increased steadily, with EQ-5D and PsAID-12 scores also improving for both groups. TNFi treated patients achieved larger improvements in PROs versus those treated with ustekinumab; however, this could have been influenced by differences in baseline measurements and factors influencing treatment decisions.
Work activity impairment, EQ-5D, and PsAID-12 scores were better in patients who achieved cDAPSA low disease activity/remission versus those who did not. Better scores were also seen in EQ-5D and PsAID-12 with cDAPSA remission, suggesting that an efficacious treatment may result in improved patient quality of life. However, further clinical trials evaluating this link are needed before conclusions can be made.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with plaque psoriasis do you see per month?

