All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The pso Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the pso Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The pso and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The PsOPsA Hub is an independent medical education platform, supported by educational grants. We would like to express our gratitude to the following companies for their support: UCB, for website development, launch, and ongoing maintenance; UCB, for educational content and news updates. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis content recommended for you
Apremilast for genital psoriasis: results from the DISCREET trial
Genital psoriasis can affect up to 63% of patients with psoriasis at some point, but is underdiagnosed and can cause a significant impact on quality of life.1 Treatment of genital psoriasis is difficult, and topical treatment can lead to side effects such as burning and pruritus due to the thinner and more sensitive skin.1 Therefore, oral systemic treatments may offer an alternative for patients who experience difficulty with topicals.1
Here, we summarize results from the phase III DISCREET (NCT03777436) trial by Merola et al.1 published in Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. The DISCREET trial compared apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, with placebo in patients with moderate-to-severe genital psoriasis.1
Study design and patient population1
- Patients were enrolled between February 2019 and September 2021, and were randomized 1:1 to either apremilast 30 mg twice daily (n = 143) or placebo (n = 146) for 16 weeks, after which all patients entered an open-label extension and received apremilast up to Week 32.
- The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a modified genital Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) at Week 16.
- Secondary endpoints included improvement in genital psoriasis Itch Numeric Rating Scale and change in Dermatology Life Quality Index.
The majority of patients were male (69.9%) with a mean age of 45 years. All patients had a genital PGA of moderate (86.9%) to severe (13.1%) at baseline.
Key findings1
- Over double the proportion of patients in the apremilast group achieved the primary endpoint compared with placebo (Figure 1).
Figure 1. A Proportion of patients achieving a modified genital PGA, B GPI-NRS response rate, and C DLQI mean change from baseline*
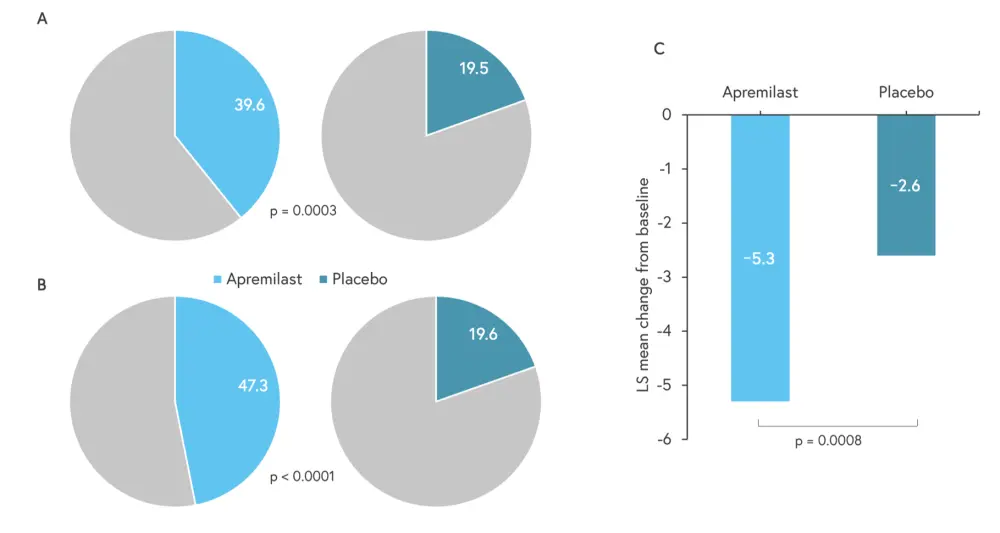
DLQI, Dermatology Life Quality Index; GPI-NRS, Genital Psoriasis Itch Numeric Rating Scale; LS, least squares; PGA, Physician’s Global Assessment.
*Data from Merola, et al.1
- More patients experienced treatment-emergent adverse events in the apremilast group (72%) compared with placebo (57.2%).
- The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were:
-
- Diarrhea (8.3% placebo vs 25.9% apremilast)
- Headache (11.0% placebo vs 23.1% apremilast)
- Nausea (7.6% placebo vs 22.4% apremilast)
- Nasopharyngitis (8.3% placebo vs 8.4% apremilast)
|
Key learnings |
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with psoriatic arthritis do you see per month?

