All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The pso Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the pso Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The pso and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The PsOPsA Hub is an independent medical education platform, supported by educational grants. We would like to express our gratitude to the following companies for their support: UCB, for website development, launch, and ongoing maintenance; UCB, for educational content and news updates. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis content recommended for you
The epidemiology and risk of mortality for patients with psoriatic arthritis
Do you know... Which continent has the highest prevalence of PsA in patients with psoriasis?
Prevalence and incidence of PsA in general population1
In the general population, the prevalence of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) ranges from 0.1% to 1% worldwide. A high degree of variability has been observed between epidemiological studies, partly due to the geographic location and due to the use of different definitions of PsA. In Japan and Norway, the estimated prevalence of PsA has been recorded as 1 and 670 cases per 100,000, respectively. A high degree of variation in PsA incidence has also been found both between and within continents (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Incidence of PsA in the general population*
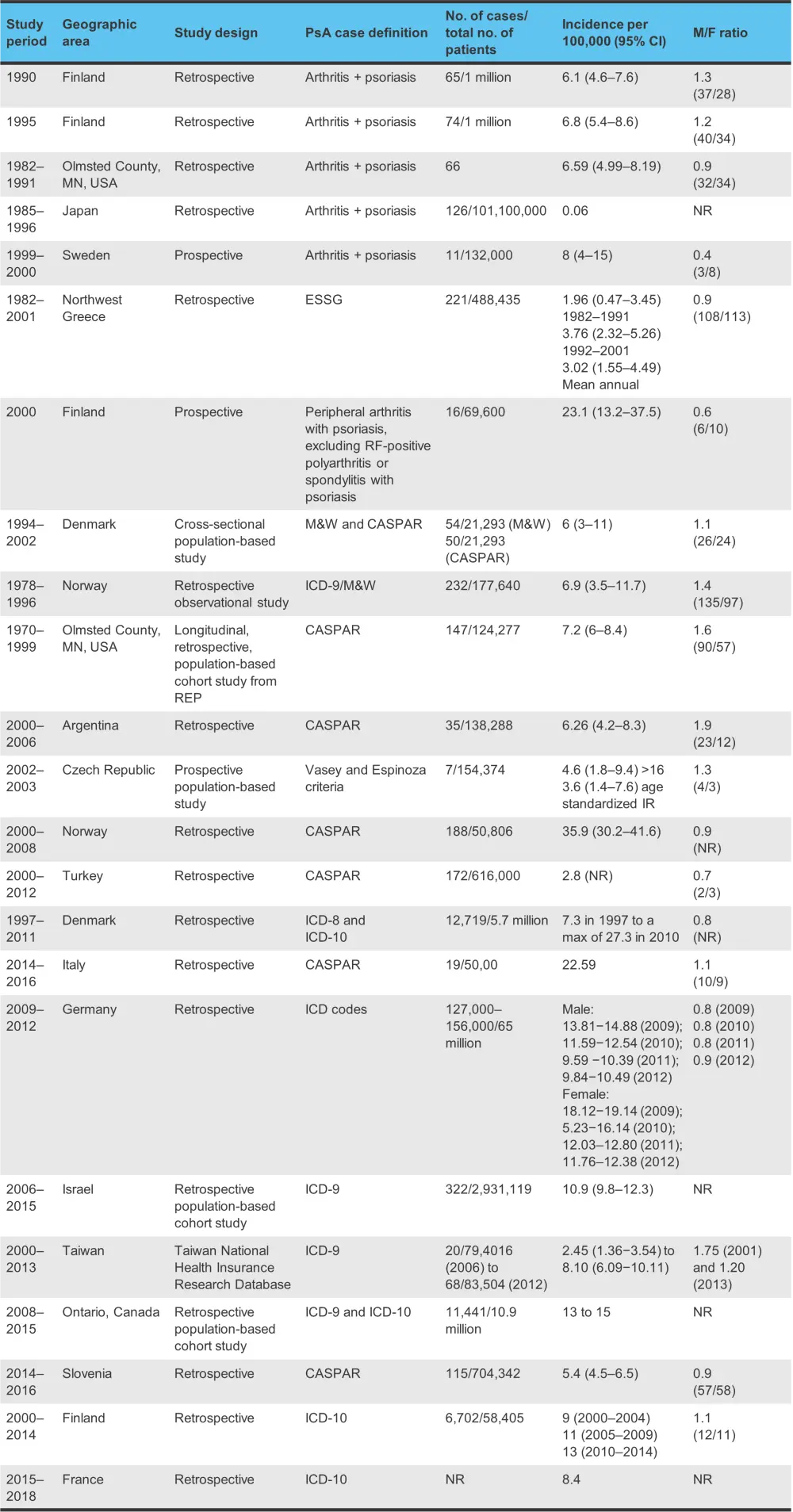
CASPAR, Classification of Psoriatic Arthritis; CI, confidence interval; ESSG, European Spondylarthropathy Study Group; ICD, International Classification of Diseases; M/F, male to female; M&W, Moll and Wright criteria; NR, not reported; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; RF, rheumatoid factor.
*Adapted from Karmacharya, et al.1
The ClASsification of Psoriatic ARthritis (CASPAR) criteria was developed in 2006, which provided some uniformity in defining PsA, though not all studies use this system as it requires a physical examination of the patient. Studies that used the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes found the lowest prevalence of PsA, whereas studies that used self-reported PsA diagnoses reported the highest prevalence.
Most studies of prevalence trends of PsA have shown an increase in recent years. No clear sex predominance has been identified, with studies from different countries finding opposing results. For example, a higher prevalence in males was recorded in Norway and Argentina, whereas in the Czech Republic and Denmark, a greater prevalence of PsA was noted in females.
PsA prevalence and incidence in patients with psoriasis
In patients with psoriasis there is also variability in the prevalence of PsA recorded by different studies. One study reported a prevalence of PsA in patients with psoriasis of 19.7% (95% confidence interval, 18.5−20.9%), with adults having a much higher prevalence than children/teenagers at 21.6% vs 3.3%, respectively. In addition, a higher prevalence of PsA was noted in patients with moderate to severe (24.6%) compared with mild (15.8%) psoriasis.
The prevalence of PsA in patients with psoriasis has been shown to be variable between continents:
- Asia, 14.0%
- Africa, 15.5%
- North America, 19.5%
- South America, 21.5%
- Europe, 22.7%
The incidence of PsA among patients with psoriasis is also varied, ranging from 1.7% to 7.4% (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Incidence of PsA among patients with psoriasis*
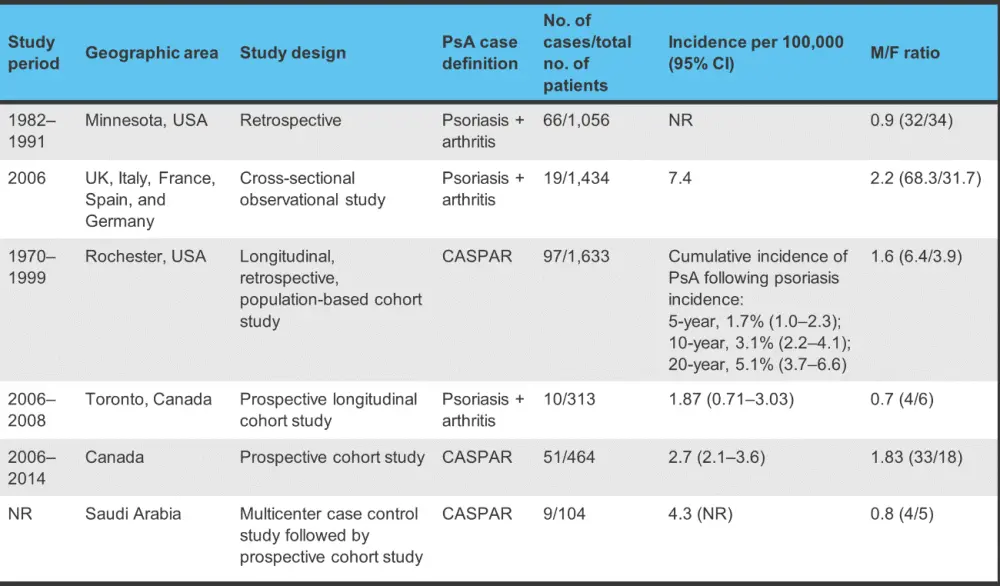
CASPAR, Classification of Psoriatic Arthritis; CI, confidence interval; M/F, male to female; NR, not reported; PsA, psoriatic arthritis.
*Adapted from Karmacharya, et al.1
Mortality
Evidence regarding the impact of PsA on mortality is conflicting, with the standardized mortality rate (SMR) varying from 0.05 to 98.5 (Figure 3). Older studies may show a higher SMR than more recent ones.
Figure 3. Mortality of PsA: overall and cause-specific*
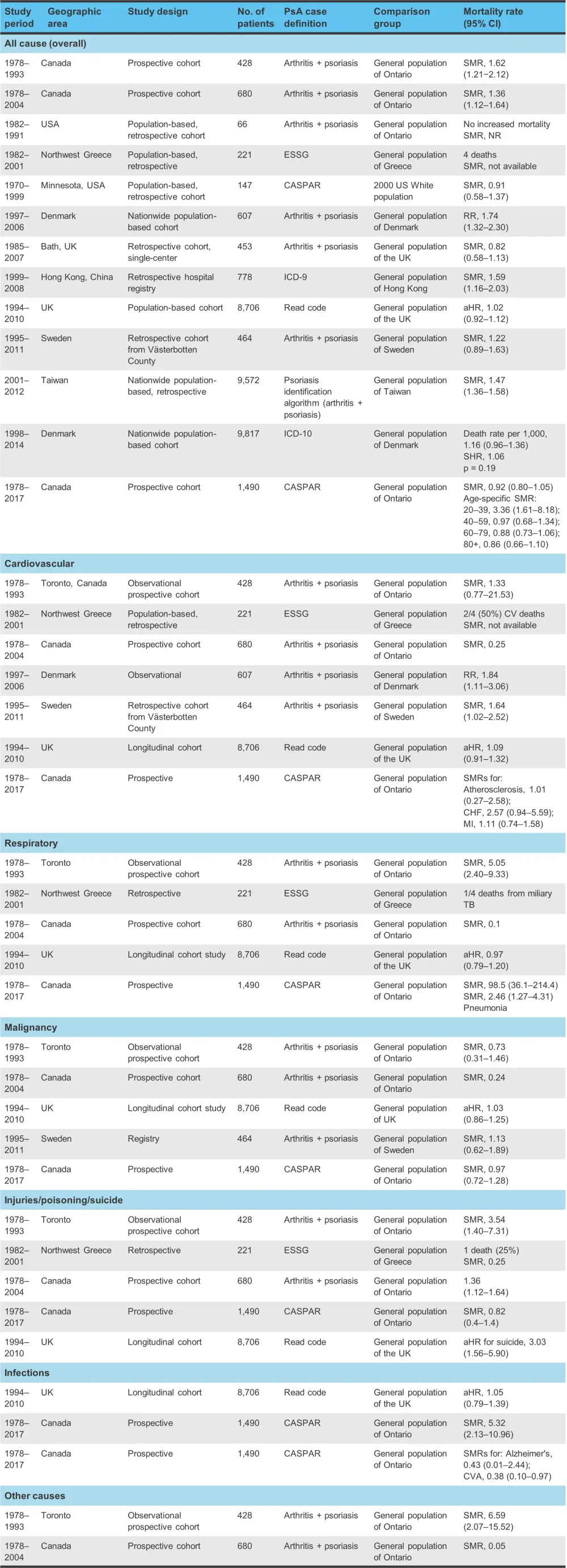
aHR, adjusted hazard ratio; CASPAR, Classification of Psoriatic Arthritis; CHF, congestive heart failure; CI, confidence interval; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; ESSG, European Spondylarthropathy Study Group; HR, hazard ratio; ICD, International Classification of Diseases; MI, myocardial infarction; NR, not recorded; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; RR, relative risk; SHR, standardized hazard ratio; SMR, standardized mortality rate; TB, tuberculosis.
*Adapted from Karmacharya, et al.1
A prospective study from the University of Toronto has demonstrated decreased mortality risk over time across almost four decades of follow-up:
- from 1978 to 1986, the SMR was 1.89;
- from 1987 to 1995, the SMR was 1.83;
- and from 1996 to 2004, the SMR was 1.21.
A more recent study from 1978 to 2017 showed no increase in overall mortality rate, with an SMR of 0.92 (95% confidence interval, 0.81−1.05). While evidence is currently contradictory regarding the impact of PsA on cardiovascular mortality, some studies have shown an increase in risk. Occasionally, cause-specific mortality for respiratory diseases has also been linked to PsA; however, again the data are conflicting.
Conclusion
While an increasing trend in PsA prevalence has been seen in recent years, PsA remains underdiagnosed. The development of PsA is complex and multifactorial. Overall mortality does not appear to be increased in patients with PsA; however, there is an increase in certain cause-specific mortality groups such as cardiovascular comorbidities.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with plaque psoriasis do you see per month?

